I tweeted about conference programmes and schedules as an access issue and enough people said it was useful that I want to write about it in a less ephemeral way. If this post helps you, please share it and link to it!
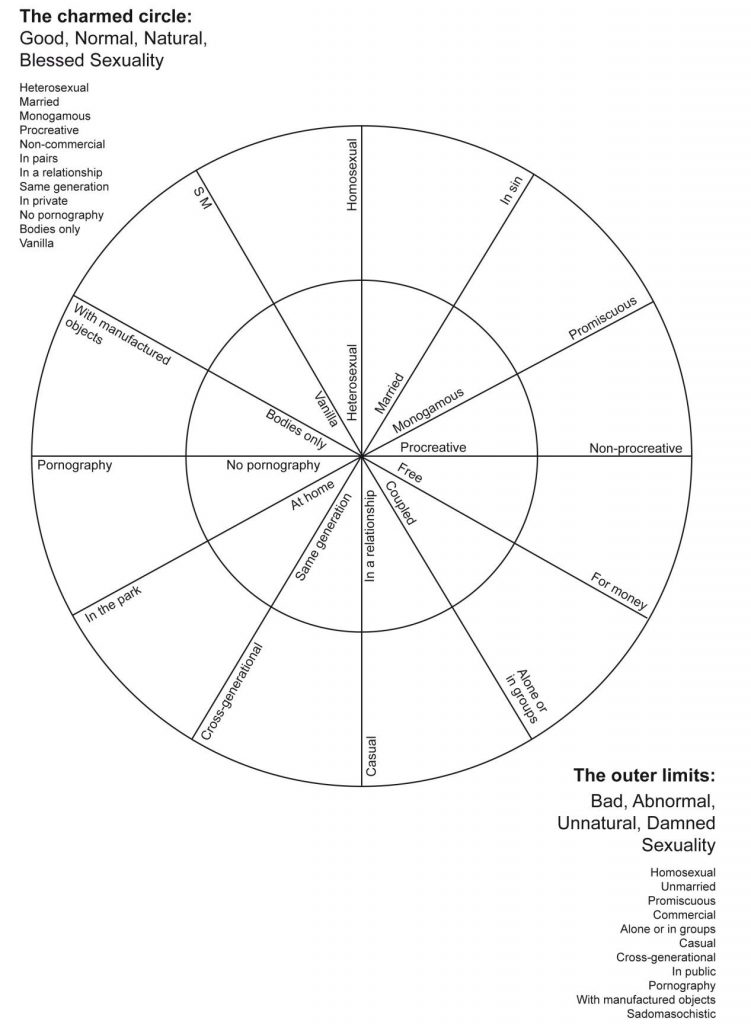
I’m coming from this from a disability-aware and accessibility perspective. I know that sessions running over is frustrating for most people and causes chaos if there are parallel sessions/tracks. However, I don’t think there’s enough written about how poor scheduling can make a conference inaccessible to people with disabilities, people with caring responsibilities, and people who have needs that are not necessarily thought about, such as people who use gender neutral toilets or people working more than one job. I use the word “maybe” throughout this post to indicate that one cannot know someone’s access needs based on appearance: we cannot assume that no one attending a conference (whether that’s academic, activist, policy, industry or something else) will experience these or similar issues.
I have based this post on things that I’ve experienced myself or that I’ve helped others navigate, but I’m inevitably going to miss things. If you feel able, I’d love to hear about your experiences in the comments.
Access breaks:
Please stick to these! If they’re in the programme, I have already factored them in and have planned my needs around them.
Maybe I need extra time to find and use an accessible or all gender toilet. Maybe I have health issues or use medication that mean I need to use the toilet more frequently. However, access breaks don’t necessarily mean toilet breaks. I may need to use the access break to check my blood sugar and administer insulin. Maybe I need to phone home to check my kids are okay. Maybe there’s something else that means that a cancelled or shortened access break makes things difficult for me.
Access breaks are also essential for making connections with potential colleagues, collaborators and friends! Having to do this in ten or fifteen minutes can be really stressful – longer breaks give people time to relax.
Lunch:
Someone said in the twitter responses that they’d attended a conference that ended up running overtime so the organisers decided that the best way to avoid time creep was to cancel the lunch break. DO NOT DO THIS.
I may have diabetes. I may use medication that must be taken with a meal. I may need the time to move around and stretch. I may need to phone someone I care for to make sure that they’re okay. I may need the time to work – perhaps I’ve arranged a skype call or on-campus meeting and need to slip away. At the very least, people don’t concentrate well when they’re hungry and no one wants to present to a room of hangry attendees.
Also, label your food with allergens; no one wants to play Allergy Roulette. You always need to order more vegetarian/vegan food than there are vegetarian/vegan attendees because all the meat-eaters look at our food and go “ooooh, that looks nice, I’ll have that” and then there is no food left for the vegetarians and vegans. This makes me both hungry and sad :(
Sessions/panels:
Please keep to the timetabled sessions, whether it’s a series of individual papers of 20 minutes + 10 minutes for questions, or a panel/discussion of a given length. Going over means not everyone gets the same amount of time to speak (which is deeply unfair, and often penalises younger, early career and/or less established presenters) but again, is also an issue of access and inclusion.
Maybe I have joint issues which mean that sitting for a length of time will cause me pain and I’m relying on being able to move around and stretch after a known amount of time. Maybe I have a cognitive processing issue which means that I struggle to take in a lot of dense information at once. Maybe I have fatigue issues and am counting on being able to skip a paper to get some rest and then return for a paper that I want to attend. Maybe I have a visual or hearing issue that means that trying to focus on a screen or speaker’s voice will exhaust me after a while. Maybe I was counting on being able to leave at a suitable break in the day (for example, after a session or panel) because I have other commitments – a meeting elsewhere, another job to get to, or caring responsibilities.
Some of the conferences I’ve attended have factored in five minute breaks between papers in a parallel session to allow people to move between rooms. This is great as it allows people some time to move between sessions/panels and to navigate an unfamiliar building. If a conference does this, those five minutes are not extra time for the speaker or for questions!
The whole day:
I’ve attended more than one symposium/one day conference that has run over by over an hour. This is enormously frustrating to everyone, such those who have booked seats on trains, coaches or planes. However, there are again issues of exclusion, especially for those with caring responsibilities or disabilities.
I may have carefully “assigned” my energy to get to and from the event and to get through the day (the spoon theory is a useful metaphor to understand the careful rationing of energy that chronically ill and disabled people do). Going over the energy that I have allocated to this event (using up too many spoons, to use the metaphor) may mean I tip into being too fatigued to get home safely by myself. This may result in more expense for me because I’d need to use a taxi rather than the public transport I had intended to use. I may have caring responsibilities e.g. a child, a parent or a partner and they are depending on me being able to take over their care from a certain time. I may have a health issue which means I am really carefully trying to avoid rush hour public transport: I may be trying to avoid the rush hour due to sensory overload, I may need a seat, or I may need to get a mobility device on a bus or train. I may be working at another job and need to be there in time for my shift. Maybe – and who would have thought this in academia with its notoriously bad work/life balance – I have social plans that I’ll need to cancel or rearrange
I may find deviating from the known schedule stressful or disorientating. This is one issue that affects me in a big way, and one that’s easy to underestimate. At events that have significantly gone over, I start fretting about how the organisers will respond, what’s going to be cut, whether an access break is going to be cancelled, whether the conference is going to run over, how I’m going to have to manage my time in response to it going over and so on. It stops me enjoying and listening to the presenters.
Conference organisers may decide to push everything back and to reschedule things on the fly. But if everything’s pushed back by an hour and I have to leave at 16:30, that means I may miss the keynote or the session that I really wanted to attend.
If you are organising a conference:
Good, thoughtful conference programming is an access issue.
- Don’t try to squeeze in more than you can actually do because it will look good on the programme – for example, I’ve never known anyone to stick to a 10 minute slot. Instead, be realistic about how much you can do in an event.
- Don’t see access breaks and lunch as optional.
- Be strict with your speakers and make sure that your session chairs feel supported by you and able to intervene if a speaker goes on for too long.
- Be aware that people are relying on your programme to manage their energy and other commitments