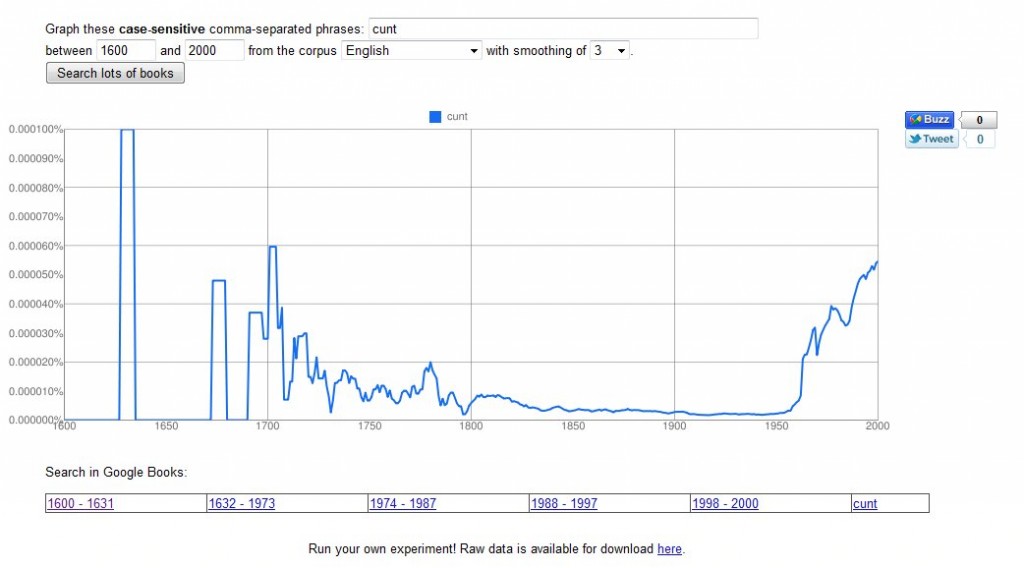
LGBT History Month starts tomorrow, and perhaps fittingly I read this footnote a few days ago.
Rosen 1974, footnote on page 209 regarding Christabel Pankhurst’s sexual and emotional relationships:
Christabel may well have been a Lesbian, but the evidence is circumstantial rather than explicit: she never married, and the copious documents relating to her life and career do not allude to any heterosexual involvements. All the available evidence indicates she had stronger emotional attachments to women than to men, and the markedly dominant/submissive character of her relationships with Mrs Tuke and Annie Kenney certainly seems to resemble the psychology of many Lesbian relationships. There is, however, no reason to believe that Christabel’s affection for Mrs Tuke and Annie Kenney ever involved conscious sensuality, and as far as the history of the WSPU is concerned the exact nature of Christabel’s sex-life is less significant than the fact that by 1913 she had grown into a state of mind in which she was completely adverse to any form of co-operation with men.
I find it an interesting footnote for several reasons: the first and perhaps most immediately obvious reason is the speculation as to the dynamics of lesbian relationships. Without further information it’s difficult to say whether this observation has anything to do with the perceived dynamics of butch/femme relationships, but I do find it interesting that lesbian relationships are markedly dominant/submissive, and heterosexual ones are not marked in the same way.
Secondly, it was published in 1974; academic research also has a historical context. 1967 marked the passing of the Sexual Offences Act and the decriminalisation of homosexuality in the UK, and this book was published seven years after that. I don’t want to read too much into a single initial capitalisation, but Lesbian suggests something about how that identity was conceptualised – as something static, as something still close to criminalisation and pathology.
Thirdly, as my last post discusses, there’s a transience in how sexual identities are understood. Our understanding of lesbian identities have already changed between Rosen’s 1974 comment and as I write this in 2011 – I think there’s a belief now that same-sex relationships are more equal than heterosexual ones. There’s more understanding of asexual identities and what these can encompass – grey-A, demisexual, homoromantic. But the context, as well as making it difficult for us to understand an individual’s sexuality in our terms, also affects how an individual would have expressed their sexuality. While sex between women was not a criminal offence, it’s not hard to imagine that the early 20th century was not the most lesbian-friendly of times.
Fourthly, I like how it delivers what Dr Lesley Hall describes as a “codslap”. This footnote reads like a response to others’ speculation as to Christabel’s sexuality, and ultimately concludes that whatever her sexuality, it’s less important than how she felt about men being involved with the WSPU campaign.
For me there’s a tension between the importance of acknowledging historical figures’ non-heterosexual identities when we have evidence for them – people like Alan Turing and Edward Carpenter – and not trying to ascribe sexual identities where there isn’t (enough of) that evidence. Short of necromancy or the loan of a TARDIS, we can’t actually know, and besides, sexuality is just one facet of a person’s identity. Other facets exist and may be more important to that person, and perhaps it’s an issue of finding a balance between sexuality being invisiblised and sexuality overshadowing other important parts of an individual’s identity. It’s something I’m still mulling over though, and I definitely don’t have anything conclusive to say.
If you’re a University of Nottingham person, we’ll have a history display in the Portland Atrium tomorrow between 10 and 4 so come along if you want to learn something about LGBT history.
PS if you do have a TARDIS, I have an interesting research proposal for you…